Release Date:2023-02-17 10:51:11 Popularity:
Intelligent manufacturing in the era of the Industrial Internet of Things, in order to improve competitiveness, manufacturers are promoting the transformation from a passive problem-solving model to a more active equipment, process, product and factory management model.
1. Industry problems faced by the manufacturing industry
Internal pressure: highly dependent on the labor force, the aging problem is expanding year by year, which is not conducive to industrial development.
Export products are still labor-intensive industries. Among them, the manufacturing chain processes such as mechanical metal processing, textiles, and electronic product production are the most labor-intensive and time-consuming. Highest error rate and worst efficiency. Many SMEs lack the capital and knowledge to introduce advanced technologies. Low birth rates and an aging population will make it increasingly difficult to recruit traditional workers, and the quality of work and living space will be even more unfavorable.
External pressure: The international scheme is mature, and intelligent manufacturing has become the development trend of major international manufacturers. Starting from the Industrial Internet of Things, we will accelerate to meet the needs of intelligent manufacturing, realize the goal of saving money, time, and labor, and quickly manufacture and ship.
In order to improve competitiveness, enterprises related to manufacturing must be digitized and automated. If there is no excellent integrated solution in China, we can only use foreign solutions in the future. Not only will it be difficult to give full play to our unique competitive advantages, but we will also lack the opportunity to create the output of whole plant solutions.
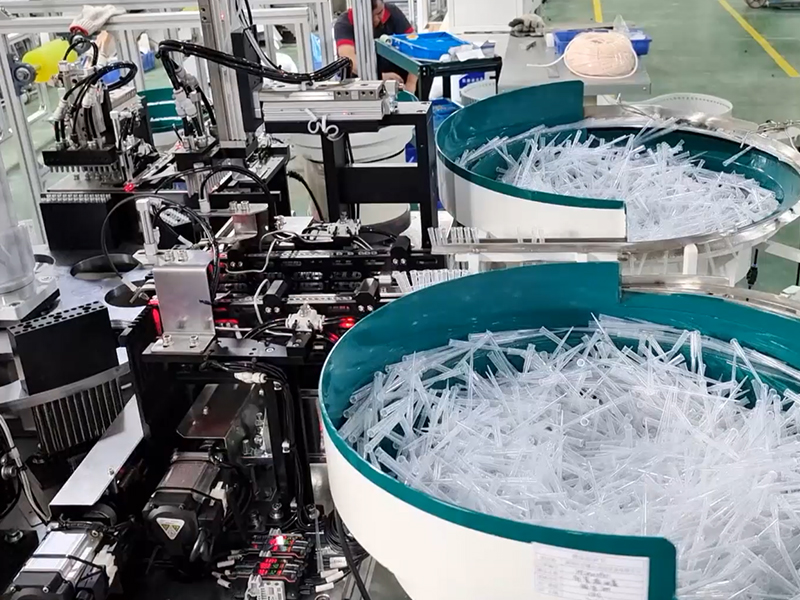

2. Four elements of intelligent manufacturing
Imported automation equipment: Although automation equipment is one of the foundations of intelligent manufacturing and can replace some manual-based work, the most important thing is to match and optimize all aspects of design, production, and service in order to have an efficient and low-cost process.
Equipment connection and data integration: After the automation equipment is imported, the next step is to connect the equipment. Through the Internet of Things technology, the data of each device can be integrated to optimize the manufacturing process.
Remote monitoring: Although smart manufacturing has replaced some manual work, people can therefore carry out more decision-making and technical work, and help operators keep abreast of the status of equipment through remote monitoring. Adjust manufacturing plans in real time, reduce equipment downtime without warning, improve production efficiency and extend equipment life.
Combining AI technology: The goal of smart manufacturing is to combine artificial intelligence, which is one of the most important trends at present. AI can upgrade equipment, and through self-learning, it can collect various information and continuously optimize the process.
3. Trends and advantages of future intelligent manufacturing
Expansion of 5G applications: The three major features of 5G are expected to provide safe, fast, and highly reliable communications, and promote the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry to smart factories. It is necessary to jointly develop surrounding supply chains and ecosystems with telecom operators, system integrators, and Netcom operators. In the future 5G+AI innovation scenario, ten thousand edge devices within one square kilometer may be connected in series within one second to make optimal decisions in a timely and effective manner.
Introduce AI explainability: Humans and machines cooperate obviously, and they must rely on explainability to convince people and assist analysis and decision-making. When it comes to process-specific optimization and selection of important features, model judgment results can be difficult to convince process engineers with years of experience. In addition to the high process cost, the ability to propose explainability at this time plays a key role in whether the application can be realized.
Federated learning model: mainly for AI model training, due to considerations such as privacy, regulations, geographic regions, and industry competition in the data set, traditional centralized learning cannot be performed. Therefore, model sharing is used instead of data sharing to break data barriers and achieve application. End-to-end differentiation and knowledge sharing. In terms of local intelligent manufacturing, it can be considered to introduce it into industrial clusters dominated by small and medium-sized enterprises. These small and medium-sized enterprises have common AI needs, but need product differentiation.

Information Security Protection: The most common security threats in the manufacturing industry are ransomware, malware attacks, and phishing attacks. In the future, enterprise defense will shift to a new architecture that integrates IT and OT, allowing OT to incorporate information security protection, establishing a unified solution, and alleviating the challenges of digital transformation.
Benefits of Smart Manufacturing: The benefits of smart manufacturing are many, including the ability to proactively detect and respond to incidents, improve quality and yield, reduce downtime, and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). With a digital clone of the factory, new processes can be simulated in advance and where bottlenecks are found. Smart manufacturing allows for proactive changes to supply chains and smart inventories, optimizing other factory logistics, including packaging and shipping.
Smart manufacturing can also uncover new business opportunities, revenue streams, and asset monetization for sustainable competitive advantage. It coordinates and predicts the likelihood of product failure for preventive maintenance to prevent downtime. Smart manufacturing can process and analyze data in real time near the point of data generation to quickly respond to abnormalities in the process.

Smart manufacturing can help forecast demand, optimize inventory, and monitor suppliers in terms of supply chain optimization. Supply chain organizations have used analytics for forecasting and inventory management for years, but in the age of the Internet of Things, we now know where almost everything is and require more immediate capabilities. 5G networks can support ultra-high connection densities of tens of thousands of endpoints, enabling truly large-scale use of industrial data and taking factories to a new level.
Intelligent manufacturing can improve the quality of products and processes through intelligent statistical process control, yield management and reliability analysis.